Starch
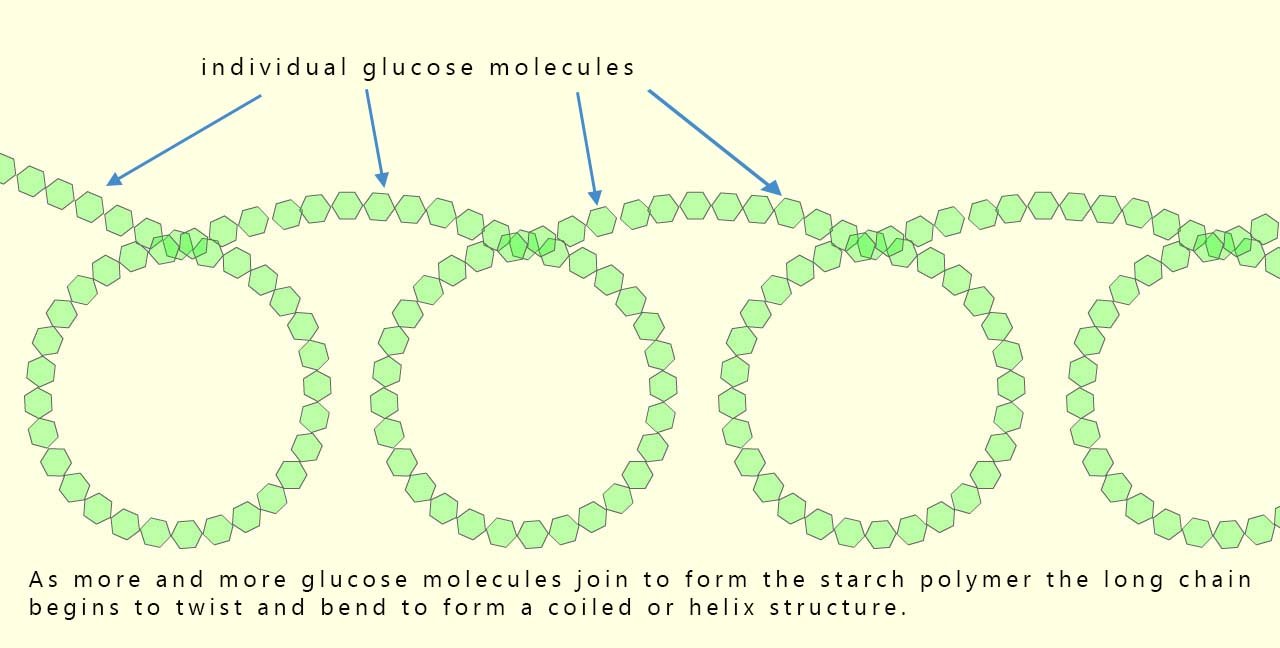
- Long chains that coil up. This makes starch compact for storage.
- Made by linking many glucose units.
- Good energy store for seeds and tubers.

Chemistry higher tier
 Carbohydrates are probably familiar to you; they are one of the main classes of foodstuffs in our diet.
Carbohydrates are found in foods such as pasta, bread, potatoes and many plant based foods.
They act as an energy source in our diets. Carbohydrates are molecules which contain only the
elements carbon, hydrogen and oxygen.
Carbohydrates are probably familiar to you; they are one of the main classes of foodstuffs in our diet.
Carbohydrates are found in foods such as pasta, bread, potatoes and many plant based foods.
They act as an energy source in our diets. Carbohydrates are molecules which contain only the
elements carbon, hydrogen and oxygen.
There are two main types of carbohydrates; these are simple
sugars such as glucose or sucrose and polymers such as starch and cellulose.
The monomer needed to make the polymers starch and cellulose is the simple sugar glucose. Glucose is made in the
leaves of plants by photosynthesis. The glucose is used as a source of energy by the plant but
some of this glucose will be converted into the polymer starch. The starch is stored in many parts of plants and
it will be hydrolysed (broken down) back into glucose sugar and used as an energy source when required by
the plant cells.
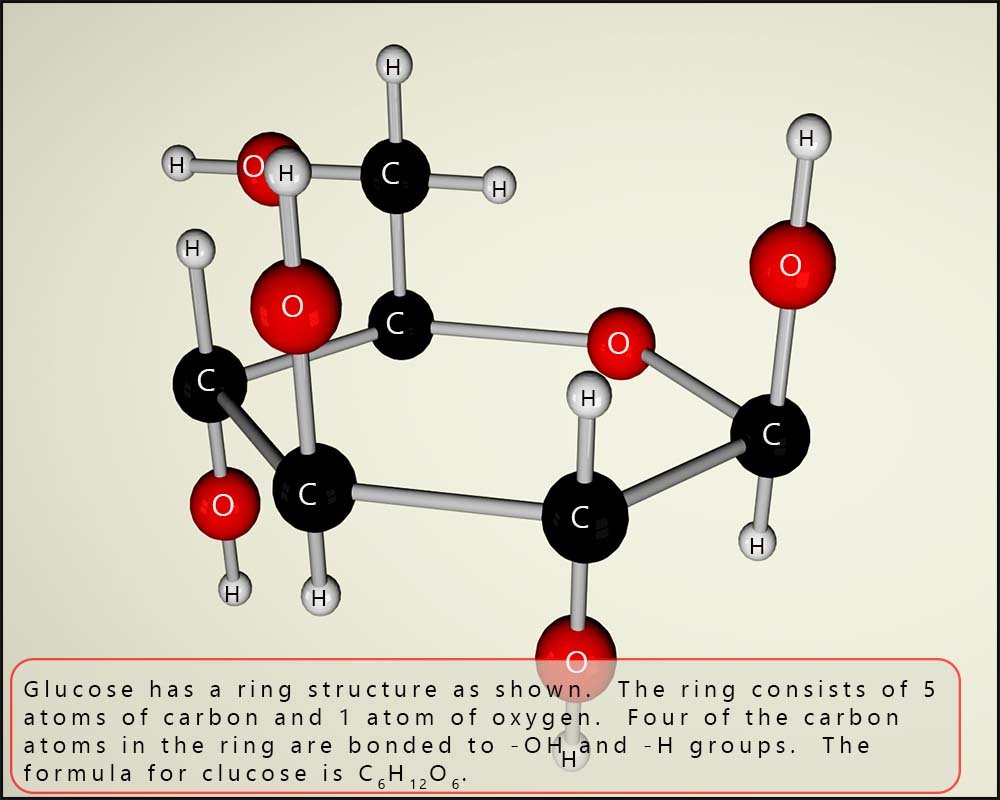
The image below shows a model of the sugar glucose; perhaps the first thing to note is that it has a ring structure. The ring consists of 5 atoms of carbon and 1 atom of oxygen. If you count the atoms present you will see that there are 6 atoms of carbon (black balls), 6 atoms of oxygen (red balls) and 12 atoms of hydrogen (white balls). This means glucose has the formula C6H12O6. It is worth mentioning that the hydrogen and oxygen are present in the ratio of 2;1; exactly as in a molecule of water. You will find this often in the formula of many sugar molecules.
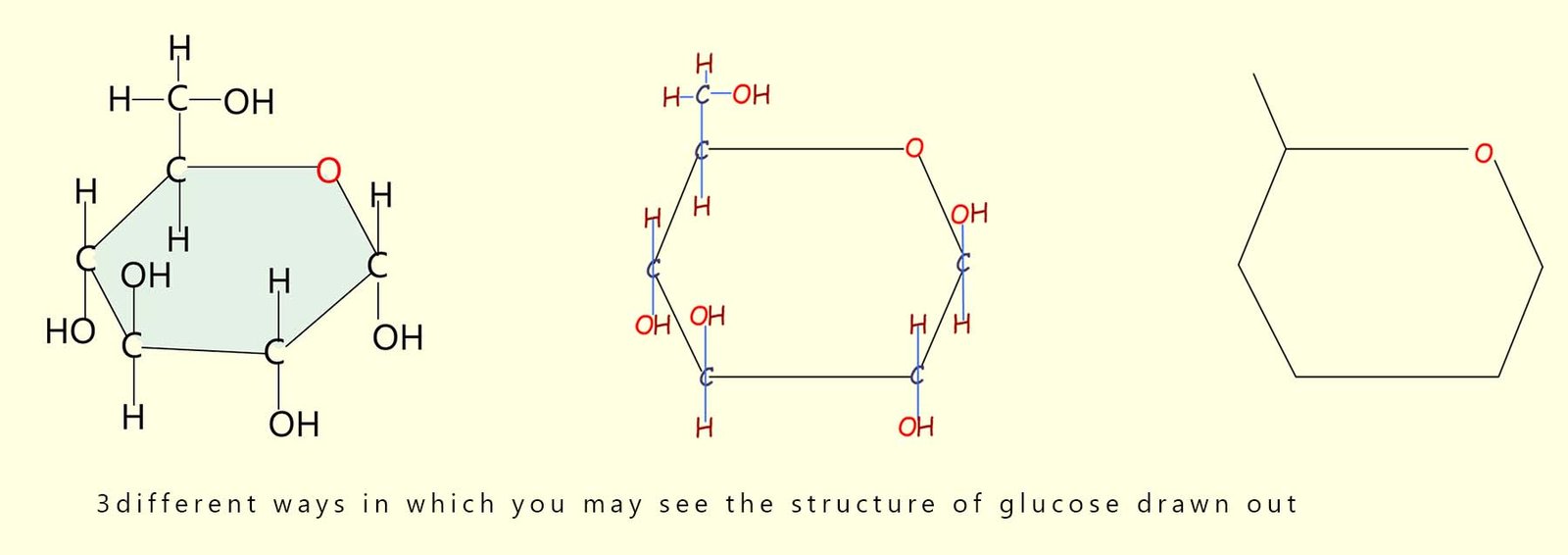
In fact you may even see the formula of many sugars written as Cx(H2O)y. For glucose x and y would be 6; to give the formula C6(H2O)6 which is just a simple way of writing C6H12O6. Sucrose, the sugar we add to sweeten tea and coffee has the formula C12H24O12; here again the hydrogen and oxygen atoms in this sugar are present in the ratio of 2:1. We can simplify its formula to C12(H2O)12. Drawing out a molecule of glucose as shown in the image above would take too long; so instead a shorthand method is used; the drawing below shows three ways in which you may see the structure of glucose drawn out.
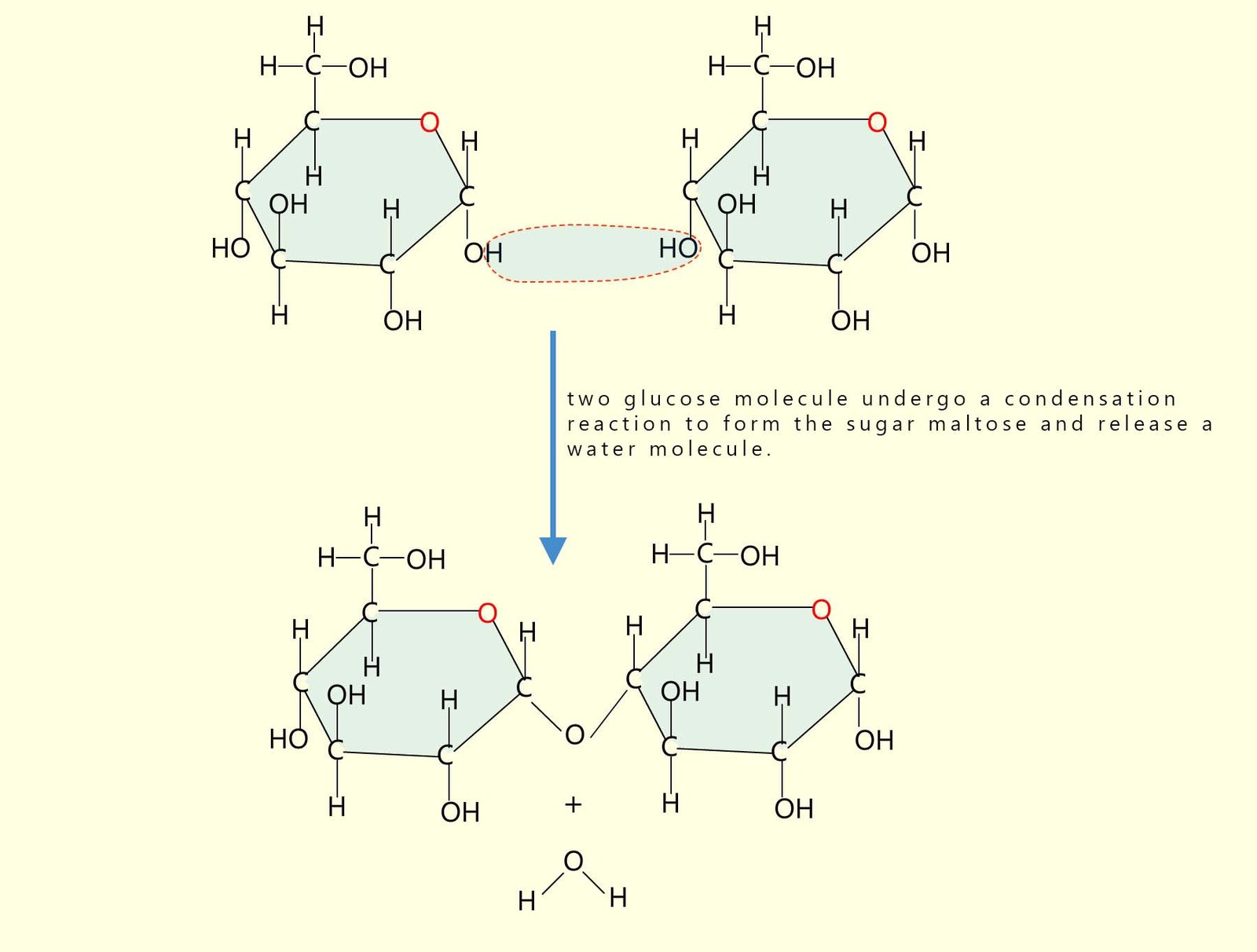
Starch is a polymer and also a carbohydrate made by joining together hundreds and in some cases thousands of glucose molecules to produce a large polymer molecule. The glucose molecules are able to undergo a condensation reaction; that is a reaction where two small molecules join to form a larger molecule and release a small molecule at the same time; in this case the small molecule is water. For example the diagram below shows two small glucose molecules joining together in a condensation reaction to form a new larger sugar molecule called maltose and at the same time release a water molecule.
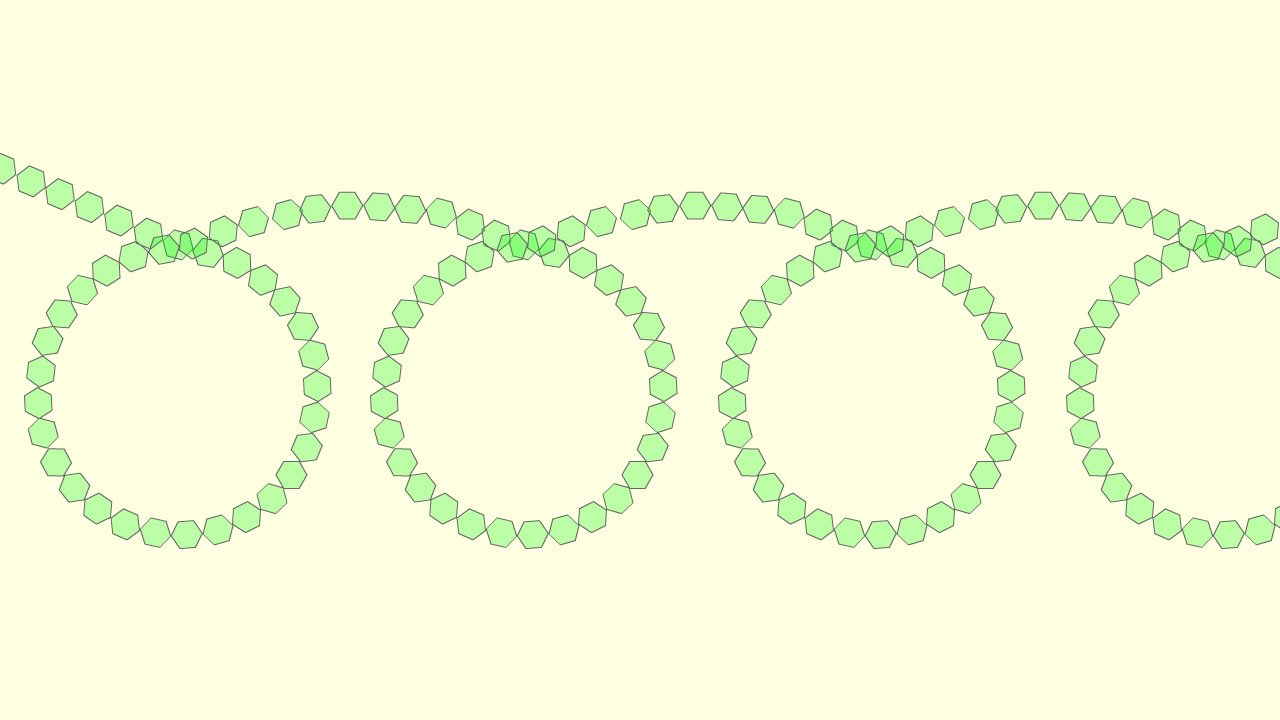
To produce starch instead of only two glucose molecules combining we need hundreds of them to condense together to form a long polymer chain; now as the long chain of glucose molecules gets longer it starts to twist due to the angle present between the bonds formed between different glucose molecules in the polymer chain, this results in the formation of a compact, three-dimensional helix (coil). This coiled structure (shown in the image below) makes starch a good compact energy storage molecule; it makes the molecule compact, so a lot of energy can be stored in a small space.
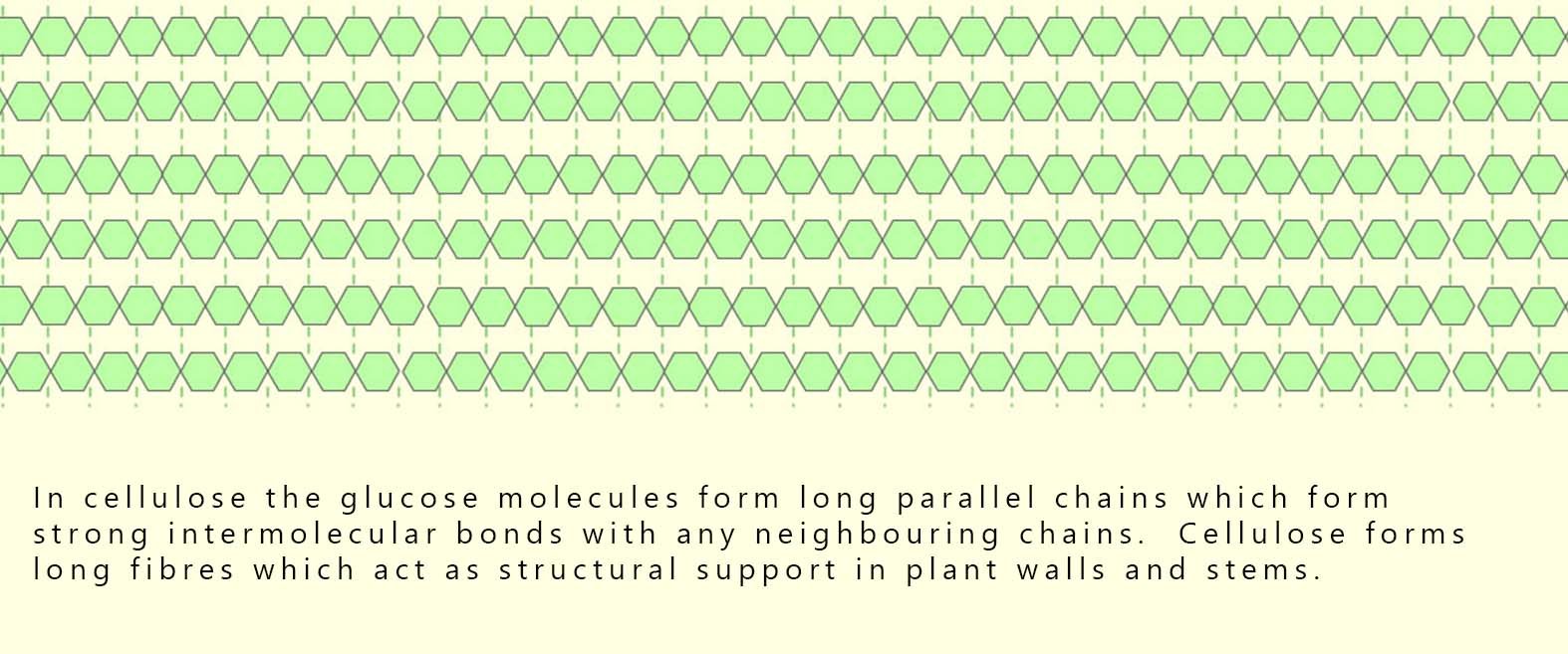
Cellulose is another carbohydrate polymer found in the cell walls of plants. It provides rigidity and strength to the plant 🌳. Its structure is very similar to that of starch in that it is a polymer made from the monomer glucose. However In cellulose, the glucose molecules form long, straight chains. These long chains of glucose molecules lie parallel to each other and are linked by strong intermolecular forces with neighbouring chains. These strong intermolecular forces cause the chains to pack together tightly to create powerful, robust structures called fibres. These long fibres gives cellulose high strength; making it ideal as the main structural material in plant cell walls, providing plants with support and rigidity.
The diagram below shows how the glucose molecules link to form long parallel chains or fibres in cellulose.
Review your understanding of the uses and structure of starch and cellulose by completing the activity below; simply click and place or drag the statements into the correct bin:
Drag each card, or click a card and then click a box.
Use the activity to quickly review the uses, properties and structures of starch and cellulose.
Switch between structure, role and food examples.

